On my iPhone, I can find my MAC address by going into Settings, then General, then About. The wifi MAC address is listed under 'Wi-Fi Address'. It's likely that the MAC address for the iPad is in the same location.
- How To Find Mac Address On Laptop
- How To Figure Out Mac Address For Wifi
- How To Figure Out Mac Address For Wifi Router
- You can buy a wireless analyzer. Use a directional antenna, and have the analyzer set to identify the MAC in question. You then triangulate the MAC to identify the location. This assumes the MAC is on your local network.
- MAC Address is a 48 bits address field. So it can hold 2^48 MAC addresses in all. MAC Addresses are of two types-a. Universally administered addresses – This is assigned by the manufacturer of the NIC. Locally administered addresses – This is assigned to the device by the network administrator. MAC Addresses are of 48 bites or 6 byte.
Please follow these instructions to find the MAC Address of your Android phone or tablet:
- Swipe down from the top of the screen with two fingers.
- Tap on the Settings icon (looks like a gear).
- In the Settings menu tap the Connections/Wireless and networksarea,
- In the Connections/Wireless and networks menu tap Wi-Fi or WLAN.
- In the Wi-Fi/WLAN menu, tap Advanced in the top-right corner of the screen (You may have totap the three vertical circles or the MORE button in the top-right corner of the screen for the Advanced option).
- In the Advanced menu, scroll down to the bottom (you may have click view more) and look for MAC addressat the very bottom of the page. This combination of 12 letters and numbers make up your device's MAC address.
Please contact the Temple University Help Desk if you have any questions or experience any issues. The Help Desk can be reached by calling 215-204-8000 or by submitting a ticket through the Request Help tab on the Information Technology Services website.
 Was this answer useful?
Was this answer useful? This document describes how to determine your device'sEthernet or Wireless hardware address(es). You need to know your hardware address(es) in order toregister your device in the Princeton University Host Database.

If you need assistance following these instructions, orneed assistance determining the Ethernet or Wireless hardware address ofa platform not covered by this document, please contact the OIT Support and Operations Center(phone 609-258-HELP, helpdesk@princeton.edu).
Contents
Instructions for Some Common PlatformsWhat is an Ethernet or Wireless Hardware Address?
An Ethernet or Wireless hardware address is a number assigned to the hardware interface in (or attached to) your computer or printer. It is assigned by the manufacturer of that Ethernet or Wireless interface, not by Princeton University.All manufacturers of Ethernet and Wireless interfaces cooperate to ensure that everyhardware interface has a unique address.
If your computer has both an Ethernet interface and a Wireless interface,each will have its own unique hardware address.
An Ethernet or Wireless hardware address is a 6-byte hexadecimal number; for example:080007A9B2FC. Each byte is written as two hexadecimal digits, so thereare twelve hexadecimal digits; each hex digit is a number from 0-9 or a letter from A-F.The letters A-F may be uppercase or lowercase.
Sometimes an '0x' is written before the value to make explicit that the following value should interpreted as hexadecimal. This '0x' is not part of the value.
Ethernet and Wireless hardware addresses are often written in other forms, to make themeasier to understand. It is common separate the six pairs of hexadecimal digits (the A-F are considered hexadecimal digits,rather than letters) with colons or dashes, like: 08:00:07:A9:B2:FCor00-00-94-ba-0e-cc.When using colons or dashes to separate the address into six pairs,sometimes any leading zero in each pair of digits is dropped; e.g. 8:0:7:A9:B2:FC or0:0:94:ba:e:cc. (When dropping leadings zeroes in a hardware address, '00' becomes '0' -- you never completely eliminate any of the six pairs of digits.)
Do not confuse an Ethernet or Wireless hardware address with an Internet Protocol v4 ('IPv4')address; that's a number assigned to some computers and printers by the Princeton University, and looks something like:128.112.1.2 or 140.180.1.2. Your Ethernet or Wireless hardware address is also not your email address, which typically looks something likerfraggle@princeton.edu.
The Easiest Way to Discover a Hardware Address
Often, the fastest way to discover a device's Ethernet or Wireless hardware address is to look fora printed label. For example, if you buy an Ethernet or Wireless interface card, checkthe box it came in for a label; you may recognize the hardware addresson the label. Other times, the actual interface may have a stickylabel somewhere on it with the hardware address.If your computer or printer has a built-in Ethernet or Wireless interface, you mayfind a label attached to the back or bottom of the computer displayingthe hardware address.
If you find a label, make sure it really is a hardware address; the section above describes what an Ethernet or Wireless hardware address looks like. For example, if you see letters of the alphabet other than A-F, you can be sure you're not looking at an Ethernet or Wireless hardware address; perhaps it is a modelnumber or serial number for your computer.
In some cases, you will not find a hardware address displayed on the box, the Ethernet or Wireless interface, or the computer or printer. (Or you mayhave discarded the box, and opening the computer or printer to examinethe interface card inside may not be a good choice.) In these cases,there is usually software you can run on the computer or printer thatwill display the Ethernet or Wireless hardware address. Instructions for some popularconfigurations appear below.
Forging (Spoofing, Cloning) Another Hardware Address is not Acceptable
Many devices can be reconfigured so that instead of using the hardwareaddress assigned by the manufacturer, they instead forgeanother hardware address of your own choosing.This is sometimes called 'spoofing' or 'cloning' a hardware address,particularly when the forged hardware address is one that belongs toanother device.
Because a device's hardware address is one of the most importantways the device is identified on the campus network, forginga hardware address is not acceptable on the campus network.No device attached to the campus network should be configured to forge its hardware address;instead, every device attached to the campus network should use the unique hardware addressassigned to it by the manufacturer.
Randomized Hardware Addresses Are (Usually) Not Acceptable
Some devices automatically change their network interface's hardware addressfrom time to time, for example, by generatinga new random (or pseudo-random) hardware address. Some do so periodically.Some do so each time the network interface attaches to a different network.
Such devices do so in the belief that it promotes privacy.More often than not, such devices limit this feature to Wireless networkinterfaces.
For some devices, this is a behavior which can be user-configured;for other devices, it is not user-configurable.
For the most part, we do not support use of such deviceson the University's networks. Each device attached via an Ethernet or Wirelessnetwork interface at the University is expected to use the unique hardware address assigned by the manufacturer to that network interface, not to generate random values or to change the value periodicallyor each time it connects to a different network.
If your device allows you to configure it to generaterandom hardware addresses or to use its real hardware address, you shouldconfigure it to use its real hardware address. If your device generates random hardware addresses and offers no way to disablethis behavior, the device is not appropriate for use on the University network.
There is a specific exception where such behavior is acceptable on the University network.When a Wireless interface is probing (scanning) to locate available wireless networks,it may choose to use a random hardware address for the wireless frames it transmitsto perform those probes. The remainder of the Wireless frames the device transmits (for example, once it decides it wishesto connect to a particular wireless network) use the unique hardware address assigned by the manufacturer to that device's Wireless network interface. This behavior is acceptable.
Windows 95, 98, ME
The process of obtaining your ethernet address is fairly simple in Windows 95,Windows 98,andWindows ME.You need to have, at least, installed the Microsoft TCPIP protocol to use this method. If you have installed the MS TCPIP protocol do the following:
- Click on Start.
- Click on Run.
- In the command line box which appears, enter the following and press the Enter key:
- A box will appear with a variety of information.Check the pull-down menu near the top to verify that yourEthernet interface is selected; if it is not, then select itin this menu.
- Look for the line labelled Adapter Address.This is your Ethernet interface's hardware address.It will be written out completely as 6 pairs of2 digits separted by hyphens. Write it down.
- If your machine has a wireless card, select Wireless interface from the drop down menu. Look for the Adapter Address under this section andwrite it down.
- Click on the X in the top right-hand corner of the box to close the windows.You are now finished.
Troubleshooting
If you are unable to see your Ethernet interface in the window displayed bythe winipcfg command,refer to the OIT KnowledgeBase solution:http://helpdesk.princeton.edu/kb/display.plx?ID=5094.
Windows NT 4.0
You can find your ethernet address using Microsoft's ipconfig utility:
- Click the Start button.
- Select Programs and then select Command Prompt.
- At the C:> prompt, enter the following then press the Enter key:
- Your machine's ethernet address is listed as the Physical Address.
- If your machine has both an Ethernet and a Wireless connection, twoPhysical Adresseswill be shown in different sections. The Ethernet hardware address is listed under Ethernet Adapter Local Area Connectionand the Wireless hardware address will be listed under Ethernet Adapter Wireless Network Connection.
- To close the Command Prompt window,enter the following at the C:> prompt then press the Enter key:
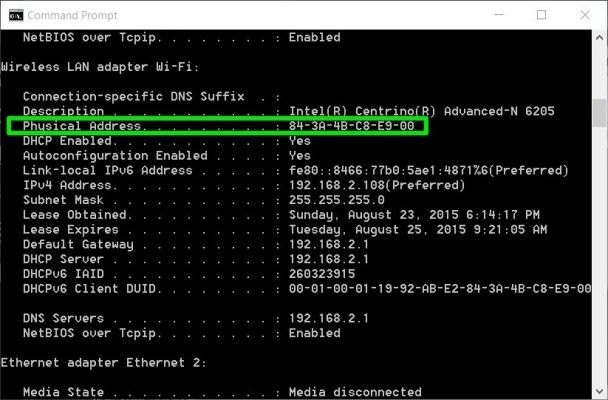
Windows 2000, XP
You can find your machine's Ethernet or Wireless hardware addresses using Microsoft's ipconfig utility:
- Click the Start button.
- Select Programs and then select Accessories/Command Prompt.
- At the C:> prompt, enter the following then press the Enter key:
- Your machine's Ethernet or Wireless hardware address is listed as the Physical Address.
- If your machine has both an Ethernet and a Wireless connection, two Physical Adresseswill be shown in different sections. The Ethernet hardware address is listed under Ethernet Adapter Local Area Connectionand the Wireless hardware address will be listed under Ethernet Adapter Wireless Network Connection.
- To close the Command Prompt window,enter the following at the C:> prompt then press the Enter key:
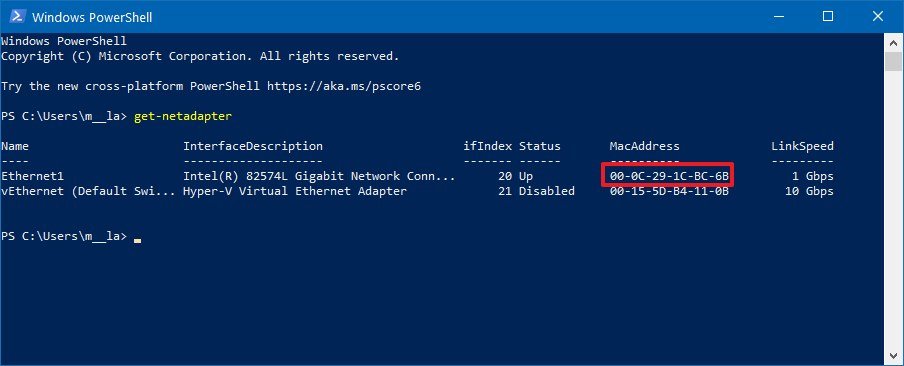
Windows Vista, Windows 7
You can find your machine's Ethernet or Wireless hardware addresses using Microsoft's getmac utility:
- If your device is a Dell laptop, ensure it is plugged into an electrical outlet;if it is not plugged in, the device's Ethernet address will not be displayed.
- Click the Start button.
- In the Search box, enter the following then press the Enter key:
- At the DOS prompt, enter the following then press the Enter key:
- Your machine's Ethernet or Wireless hardware addresses are listed as the Physical Addresses.
- If your machine has both an Ethernet and a Wireless connection, twoPhysical Adresseswill be shown in different sections. The Ethernet hardware address is listed under Ethernet Adapter Local Area Connectionand the Wireless hardware address will be listed under Ethernet Adapter Wireless Network Connection.
- To close the Command Prompt window,enter the following at the C:> prompt then press the Enter key:
Windows 8
You can find your machine's Ethernet or Wireless hardware address using Microsoft's getmac utility.
- Navigate to the Charm Bar through one of the following methods:
- Move the cursor to the bottom right corner of the screen to access the hot corner for the Charm Bar
- Windows key - 'C' command will open up the Charm Bar.
- Start a search by selecting the Magnifying Glass icon at the top.
- Search for 'Command Prompt' then press the Enter key.
- At the DOS prompt, enter the following then press the Enter key
- Your machine's Ethernet or Wireless hardware addresses are listed as the Physical Addresses.
- If your machine has both an Ethernet and a Wireless connection, twoPhysical Adresseswill be shown in different sections. The Ethernet hardware address is listed under Ethernet Adapter Local Area Connectionand the Wireless hardware address will be listed under Ethernet Adapter Wireless Network Connection.
- To close the Command Prompt window,enter the following at the C:> prompt then press the Enter key:
Apple macOS 10.12 - 10.15
To display your Apple macOS device's Ethernet or Wireless hardware addresses:
- Make sure that the network interface you're interested in is part of the current location,and is turned 'on':
- Open the System Preferences application in the Apple menu.
The System Preferences application is also sometimes available in the Dock.It's also available in the Applications folder (in macOS 10.12 - 10.15).
- Click the Network icon in the System Preferences application.
- The Network pane of the System Preferences applicationdisplays a Location pop-up menu near the top of its window.
In this Location pop-up menu, select a location that includesthe network interface of interest.
For macOS 10.12 - 10.15:You can verify that a network interface (port) is a member of a location by selectingthat location, then verifying that the network interface of interest appears in the network ports liston the left side of the window.Verify that the interface's status (which appears in grey just below the name of the interface)is anything other than 'Inactive.'
- If you made any changes in this window, click the Apply buttonin the lower right corner of the window.
- If you made any changes in the Network pane in System Preferences that youwon't want to retain, make a note of them now, so you can undo them later.
- Once you've verified that the network interface you're interested in is part of the current locationand is anything except 'inactive (in macOS 10.12 - 10.15),you can select Quit System Preferences from the File menu.
- Open the System Preferences application in the Apple menu.
- In macOS 10.12 - 10.15, launch the System Information application.
This program is normally located in the Utilities folder,which in turn is located in the Applications folder.
- The left side of the application's window is a pane listing categories and subcategoriesabout which information is available.From this pane, select Network.
- Displayed in the upper-right pane is a list of each of theMac's network interfaces that are part of the current network location and (and macOS 10.12 - 10.15) are anything except 'inactive.'(In macOS 10.12 - 10.15, these are entitled 'Active Services'.)
In this upper-right pane,select the item for the Ethernet or Wi-Fi (a.k.a. 'Wireless') interface in which you are interested.
- Displayed in the lower-right pane is information about the selected network interface.
Each interface's hardware address is the value labelled Ethernet address,MAC address, or Hardware (MAC) addressThis is true even if the device is actually a wireless interface.(It is not the item labelled RouterHardwareAddressor the item labelled ARPResolvedHardwareAddress.Make a note of the value; this is the information you were seeking.
- Quit theSystem Information application (in macOS 10.12 - 10.15),
- If earlier you changed any settings in the Network pane of System Preferences(for example, to make a particular network interface active) and you wish to change it back, do so now.
Apple iOS 4.0 - 14.3
To display your Apple iOS device'sWireless hardware address:
- Open the Settings application.
- From the list of setting categories, select General.
- From the list of general settings, select About.
- The Wireless hardware address is the value labelled Wi-Fi Address.
- Leave the Settings application.
How To Find Mac Address On Laptop
Android 2.2 - 5.0.1
To display your Android device's Wireless hardware address:
- Open the Settings application.
- From the list of setting categories, select About phone.
Some vendors locate this category underneath some other category;this can vary from device to device.
This item also might be named something else, for example, About tablet.
- From the list of choices, select Hardware information.On some versions of Android, you may instead need to choose Status.
- The Wireless hardware address is the value labeled Wi-Fi MAC Address.
- Leave the Settings application.
The Office of Information Technology,
How To Figure Out Mac Address For Wifi
Princeton University
How To Figure Out Mac Address For Wifi Router
Last Updated: January 2 2021